Cervical osteochondrosis, whose concentration is noted, as can be determined by the name, in the neck, is a fairly common pathology.Cervical osteocondrosis, whose symptoms cannot always be considered unequivocally considered as this disease, taking into account the functions of its location and local processes, often lead to the treatment of other areas, these symptoms are so contradictory.
General Description
Most often, the development of cervical osteocondrosis occurs due to a sedentary lifestyle, which in particular contributes to a significant switch from physical work, albeit to a moderate degree, previously widespread to work intellectual, which in turn is accompanied by sitting work.
Generally, before we move on to the consideration of symptoms associated with cervical osteocondrosis, I would like to note that it can be seen in the differences from symptoms that accompany osteochondrosis as a whole that might not be particularly astonishing, given the anatomical traits that the specifics that interest us (themselves).
The vertebrae concentrated in the neck next to each other quite tightly.Meanwhile, the frame is located in the cervical region is not developed too well, which contributes to the factor in displacement of the vertebrae.It causes, in turn, the compression of nerves and blood vessels, which in the cervical region is more than ample.So, for example, it is here that the spine is running, with whose help the blood supply to the brain is secured (or rather, its buttocks presented in the form of an oblong brain and cerebellum).
Compression (ie compression) of the spine due to a decrease in blood circulation can provoke ischemia of the spinal cord and brain, and if we consider acute variants of such a course, even a spinal cord blow.For other, such a lesion of the artery can be judged by the appearance of symptoms in the form of a violation of coordination of movements, frequent dizziness and disorders associated with vision and hearing.
The overall compactness of the cervical ward can cause even a weak muscle tension or spine displacement will lead to pressing the nerve endings, which involves clamping in the cervix, which can also be exposed to vascular structures.Osteeth huts formed on the basis of such conditions only lead to the deterioration of the situation in view of the compactness characteristic of the cervical region.Remember our readers that the growths in small sizes formed directly on the bones are determined as osteophytes, the substances formed in the process of pathologically essentially in the hypertrophic process (that is, in the general understanding of hypertrophy - this is a process where an increase in a separate part of the body/organ works.
Cervical osteocondrosis causes the development of projections and hernias in the spine, whose effects beyond properties such as spine displacement, stress of the vertebrae and the formation of osteophites also push the nervous root and thereby lead to the development of edema and inflammation of it.As a result, to return to the compact size that the spinal canal of the Institute of Interest in us has, it is still to emphasize that the spine covers its volume completely, as a result of further compression - this time directly in the spinal canal.As a pronounced manifestation of such a second course of the disease, pain syndrome is observed.
Furthermore, osteochondrosis can also lead to pressing the brain, and given the narrow characteristic of the spinal canal in question, so much more often than when considering processes in the lower back and thoracic parts.It is noteworthy, the damage zone is reduced with cervical osteocondrosis not only to the defeat of the neck and the head itself, but also to the defeat of the limbs (according to the upper one, such a result is diagnosed much more often).Given these features of cervical osteocondrosis, he is one of the frequent causes of patients' disabilities.
So let's try to summarize where I would especially like to touch the factors that lead to the compression of the nervous and vascular structures in osteocondrosis in the cervical region.
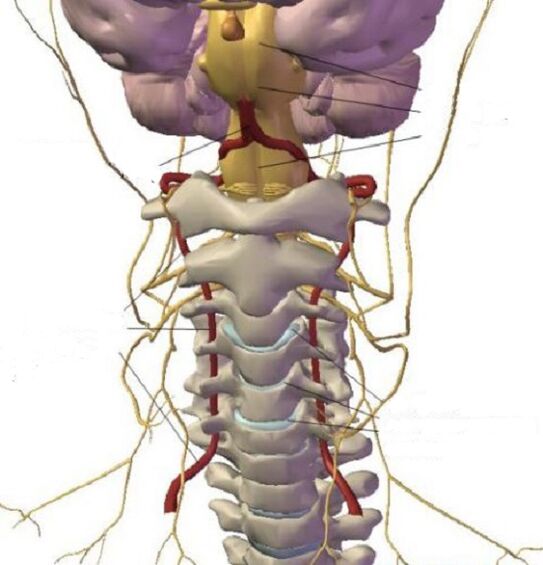
- Slides (or displacement) of the spinal cord disk.This condition involves a specific definition - Spondylolistz.For the most part, this type of displacement is minimal with regard to their occurrence in practice, in addition, it is important that even a slight shear provosing the development of paralysis, not to mention the more serious shift, leading to something else as a fatal result.
- Osteophytes.Cervical osteochondrosis, which we have already noticed, provokes the development of the corresponding growths, ie osteophytes.They are, in turn, placed from the sides of the spines leading to irritation of the muscles that directly fit them, ensuring an increase in their tone.The load affecting the vertebrae is thus increasing, this already provides an increase in pressure on the intervertebral disc at the same height.Based on such a process, the risk of projections increases.Ostepping huts aimed at the passage of the spine can provose a narrowing.
- Formation of protrusion, spinal hernia.All of this is one of the possibilities of the result of the development of processes relevant to cervical osteocondrosis.
- Changing the height of the spinal cord disk (that is, its flattening).In frequent cases, a reduction in height occurs due to a decrease in the size of the intervertebral hole.In addition, it is important to note that even a failed rotation of the neck can lead to a subluxation of the cervical vertebrae, as a result of ensuring additional compression (ie compression).
Cervical osteocondrosis: Symptoms
Changes that occur with the spine with cervical osteocondrosis occur in combination with many clinical manifestations.It is noteworthy that the list of them can be awarded about three dozen options, while the most interesting and unexpected to patients themselves may prove to be the fact that, in addition to "traditional" pain in the neck, symptoms that completely do not fall under first sight during the considered illness have to be found.So, for example, not everyone will introduce pain in the elbow joint, the weakness of the legs or visual disturbances as well as some other manifestations that we will also try to cover during the consideration below.
In order to represent the basic symptoms that can accompany cervical osteocondrosis, we convention conventionally to them three main groups determined in accordance with the dominant involvement of the central nervous system in the pathological process.
- In Group.This includes the neurological symptoms of the disease that is considered its complication that occurred due to the effect of the process directly on disks and nerve roots, as well as on the nerves and plexus (in other words, the process relates to the peripheral part of the nervous system).
- II group.In this case, we talk about the symptoms relevant to cervical osteocondrosis that manifests itself with the direct effect of the pathological process on the spinal cord.
- III group.Symptoms associated directly with the processes that occur in the brain with cervical osteocondrosis, and therefore in cranial nerves in structures and shells of its hemispheres, in the trunk and in the brain vessels.
In short, for each of the groups it can be noted that the symptoms of cervical osteocondrosis in the first group mainly have pain, the symptoms of the second are in motor disorders, and the symptoms of the third are in phenomena associated with the pathological effects of the vascular phenomena.In frequent cases, of course, there is a manifestation of these symptoms not only in their pure form, but also in terms of combined with each other, which, however, does not exclude the possibility of determining the leading group of the listed settings based on the symptoms.
Cervical osteocondrosis: Symptoms of the first group
As we have previously noticed, the first group contains symptoms in the form of painful manifestations that occur due to damage to the nervous system in the peripheral ward.This includes both constant pain in the neck (defined by both "cervical cerebrals") and cervical radiculite, cervical closes.In addition, muscles, joint pain (wrist joints, joints of elbow or shoulder), pain in the chest area may also occur (which may involve pain in the heart, liver).
It should be noted that the pain in the neck is the first symptom of cervical osteocondrosis, and it is observed in almost all patients with this diagnosis.Such pain appears in the morning after awakening and intensifies at the time of attempt to roll into a lying position as well as with laughter, cough, failed turning the head or when sneezing, which is already possible in any other position of the body.The nature of pain can be defined as a bore and stupid, in some cases, however, the pain can shoot, regardless of a particular option, the location of these pain is focused in the throat of the neck.As for pain duration, it can be either periodic and constant.
The pain that appears with awakening is subject to reduction in its own intensity that occurs during the day becomes their complete disappearance possible.Irradia of pain (its distribution) to the shoulder region and to the surface of the neck is not excluded.
The tension in the neck muscles (moderate), the difficulty of breathing in the cervical region can also be noted.The acute period of the manifestation of the disease is characterized by the adoption of a somewhat peculiar position of patients, striving to keep their heads a little under the slope forward and at the same time to the side.In the case of a shift, limitation is often observed in the rotational movements made by the head.
Frequent characteristic symptoms of cervical osteocondrosis are separated by the presence of noise phenomena that occur at the time of rotation of the head in the form of a crunch and cod, which allows you to bring an analogy with the friction of the stone on sand.Often in such cases, it is possible to diagnose the statute for the course of cervical osteocondrosis, excluded in the part of the stated symptoms of patients from attention.
In addition to cervical pain and shutter, osteocondrosis in the cervical region can occur in a complex with cervical and cervical radiculitis, these conditions are manifested in the form of pain concentrated in the upper cervical departments and in nape.Strengthening the pain is noted at the time of turning the head in one direction or another, to a lesser extent, such a manifestation of pain is relevant in other actions.Often, the spread of pain with cervical osteocondrosis occurs to the shoulder band and to the hands (to one or to both).In particular, this is currently happening by muscle tension directly related to specific nerve roots whose compression occurs of vertebrae.
For the time being, it can be noted that cervical radiculitis accounts for approx.90% of cases of pushing roots in 6 and 7 departments in 5% - in 5 and 8 departments.So the defeat of the sixth section leads to the appearance of unpleasant sensations or to the pain, concentrated within the framework of the front outer surface of the region of the forearm with a thumb;The involvement of the seventh cervical spine leads to unpleasant sensations and pain in the middle finger;The involvement of the eighth root leads to the appearance of unpleasant sensations and pain in the little finger.
If the lesion affects the upper vertebrae and cervical discs, this can lead to the involvement of the occipital nerve that innervates the skin in the process of occipital.This is manifested with pain in nape, respectively, they are constant, characterized by periodic reinforcement.The nape area also loses sensitivity, a specific pain point can be detected in the form of painful seals and stress.
Cervical osteocondrosis often leads to the development of crooked, which is due to a spasm of the neck muscles based on the head of the head and the curvature of the neck that is characteristic of this condition.In this case, the head is changed slightly to the side/forward or to the side/back.There is virtually no possibility of moving the neck, an attempt to turn against the head is accompanied by the appearance of certain pain in the neck, shoulder or back of the shoulder.
Compressing the vessels into osteocondrosis due to inadequacy for this reason for blood supply leads to the weakening of the pulse of the radial artery and with attacks of pain with the contemporary pale of the fingers.
Another manifestation of cervical osteocondrosis is a complication in which pain concentration occurs in the shoulder joint which is defined asShoulder -shoulder periiarthritis.It develops due to violations in the shoulder-location area of innerving, due to the dystrophic changes in the gradual way, qualities that are growing.These disturbances occur with the beginning of a painful process accompanied cervical osteochondrosis, but for a long time they are simply invisible.
The main symptoms of this pathology are pain in the joint, usually that occurs without visible causes, the manifestations of this pain are noted in an improved form at night.Then the abduction against the hand to pain (mainly from the outer part of the joint) leads to the probe determine the painful zones.Due to the patient's desire to secure the rest of the painful limb, the joint is stiffer on the basis of reflex muscle contraction in it ("frozen shoulder").Subsequently, in the absence of treatment, it becomes impossible to raise the hand more than over the horizontal level.
Cervical osteocondrosis: Symptoms of the other group
Symptoms of the other group consist of syndromes that occur on the basis of damage to the cervical level of the spinal cord.Two mechanisms can lead to it, it is either compression produced from the disk with a pulpose core due to the softness of its consistency, or damage to the spinal cord from the side of solid (long -lasting) disks or outgrowth from the rear neck rhyme.In women, the first more often in men is observed - the second mechanism.
Symptoms of this course are often accompanied by weaknesses in the arms and legs, and in the legs there is an increase in tone without muscle weight loss, in the hands, on the contrary, the tone is reduced, the volume is reduced.Sensitive muscle features in their hands can also develop without pain.Most often, such a complication is diagnosed at the age of 40 to 55, somewhat less often - at the age of senile and even less often - at the age of Young.The relevance of such a complication can be discussed in the presence of a patient in violations associated with cardiac activity (arrhythmias) or with atherosclerosis.
Changes that occur in the spinal cord are defined asMyelopathy, It develops on the basis of pathological changes in the disk located in the area between the 5th and 6th cervical vertebrae.Its development can provoke its development of the spine, excessive overrain that affects the muscles of the shoulder band as well as negative emotions and alcohol poisoning.
One of the varieties of manifestation of myelopathy is the disappearance of temperature and pain sensitivity due to the functions of the listed clinical manifestations.Accordingly, patients lose the possibility of feeling the irritating effects that somehow on the skin of the cervical region, the upper parts of the chest and arms (on one side).Thus, the plot that has lost the sensitivity has the form of a fence.Along with the stated symptoms, spontaneous pain (fracture, sore) occurs from the side of the defeat that the hand is weakened.
Another type of manifestations of cervical osteocondrosis is "Semiconductor Disorders Syndrome", which occurs with insufficient supply of the side columns in the spinal cord (its departments) with blood.This leads to increased fatigue of the lower extremities marked when walking/standing, as well as to intermittent chrome.Nun of the hands as well as unpleasant sensations in them (which are relevant to the daytime), in some cases such manifestations are noted in the feet not excluded.When you close the eyes, a violation of coordination arises.Despite their own constance, the listed phenomena do not limit the ability to work capacity.
Cervical osteocondrosis: symptoms of the third group
The third group of symptoms contains brain manifestations of the considered disease that occurs due to lack of blood flow in the system responsible for supplying the brain stem with blood.Vertebral arteries act as the main vessels that form such a system.We highlight the main types of syndromes that are relevant in this case.
- Hypotalamic syndrome.It is most often diagnosed, manifested in symptoms indicating decreased hypothalamus, or rather, in the form of neurotic disorders.This is irritability and increased fatigue, anxiety and touch, instability of moods and sleep disorders (its superficiality, sleep is characterized by easy to rise without a feeling of rest, difficulty falling asleep).The possibility of concentration about something is lost, the ability to remember is reduced, unpleasant sensations often appear in different organs.Serious cases are accompanied by the appearance of causal fear, anger, longing, anxiety.Patients are pale, they have a cooling of the limbs, increased sweat, increasing pressure and heart rate.The appetite, like sex drive, is reduced, urination is quick.
- Drops Syndrome.It consists of attacks from a causal decrease in a fainting of the patient with simultaneous loss of consciousness (possibly without his loss), which also occurs due to vascular spasm.Restoration of consciousness occurs quickly enough when the patient is placed in a horizontal position (the head is lowered).After an attack, patients have expressed weakness in the legs and degradation, headaches are possible.
- Vestibular-Barrel Syndrome.The only manifestation of the syndrome of the initial phase of the disease is dizziness that occurs due to the sensitivity of the vestibular apparatus to the lack of blood supply.Nausea and vomiting are possible in combination with some fluctuations in the movements of the eyeballs, instability as they walk.
- Kochlear-Tønde syndrome.It manifests itself in the form of ringing and noise in the ears, mainly on one side.The hearing may fall, the overload of the ear occurs, mainly the syndrome is associated with the previous one, but its independent course is not excluded.For other, it is not always easy to determine the compound with cervical osteochondrosis with such symptoms.
- Sydrome Gworight board.The most important manifestations consist in the appearance of the presence of a foreign object in the throat that causes difficulty in swallowing, also this feeling of dry throat is possible with itching.The voice loses its sonority, survival appears in the larynx and throat, pain in these areas.Fatigue is noted during the conversation that requires a break, difficulties in swallowing thick foods along with spasm of the esophagus are possible and reducing such manifestations occurs after rest.
- Visual disorders.Different types of visual disturbances: "Fog" in front of the eyes, a decrease in visual acuity, etc., algsing different violations during the day.
Treatment
A complete improvement in the disease we are considering is not possible because its treatment is generally focused on slowing down the current process, and especially a specific period of the course of the disease.Aggravings require hospitalization and semi -water regime.
As for drug therapy, it consists in the appointment of different types of painkillers, the possibility of using Novocaine Muscle Blocade is not excluded.In parallel with the treatment, the main emphasis of vitamin therapy, muscle relaxants can be prescribed.The effectiveness of the results in the treatment of cervical osteocondrosis is achieved by using physiotherapy methods (electrophoresis using anesthetics, ultrasound procedures, etc.).Treatment of cervical osteocondrosis also involves the need to carry the so -called Shant's collar, massage procedures are prescribed for periods of remission.
Diagnosis of cervical osteocondrosis is performed by a neurologist and the direction of this specialist can be achieved with a false assumption in the need to visit Laura, therapist, cardiologist and other specialists.
Migraine is a fairly common neurological disease, accompanied by a pronounced paroxysmal headache.Migraines, whose symptoms are actually in pain, concentrated from half the head mainly in the eye, temples and forehead, in nausea, and in some cases in vomiting, occurs without reference to tumor formations of the brain, to stroke and serious head injuries, although it may indicate the relevance of certain pathologies.
The syndrome of chronic fatigue (Sokr. Cu) is a condition where mental and physical weakness occurs due to unknown factors and lasts from six months or more.In addition, chronic fatigue syndrome, whose symptoms are to be associated with infectious diseases, is closely associated with an accelerated life tempo and an increased flow of information that literally collapses on a person for their subsequent view.
Ischemic stroke is an acute type of cerebrovascular cerebral circulation due to inadequacy of calculation to a particular area of the blood brain or to the complete cessation of this process, in addition it is damaged by brain tissue in combination with its functions.The ischemic stroke, whose symptoms as well as the disease are even observed among the most common types of cerebrovascular diseases, is the cause of subsequent disability and often fatal results.
Avitaminosis is a painful state of a person that occurs as a result of an acute lack of vitamins in the human body.Distinguish between spring and winter vitamin deficiency.There are no restrictions on the floor and the age group, in this case.
Asthenotgetative Syndrome (ABC) is a pathological process in which a functional violation of the autonomous system takes place, which is responsible for the function of internal organs.Most often, such a violation arises as a result of a person's inability to respond adequately to stressful situations.
With the help of physical exercises and abstinence, most people can cope without medication.


















































